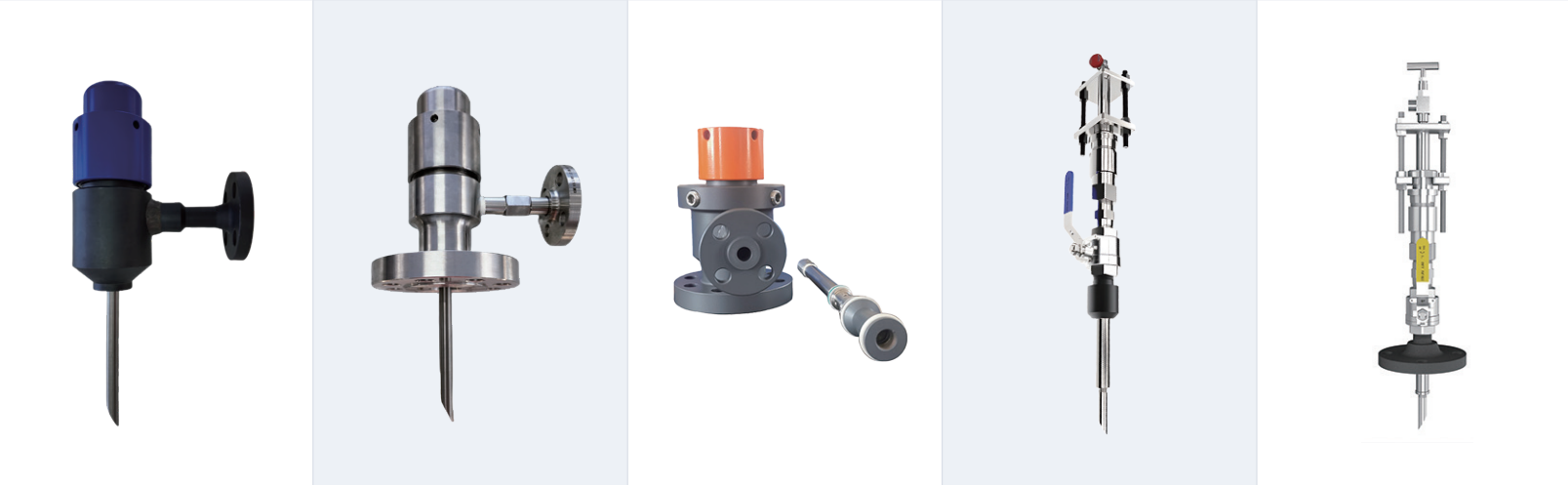
Description
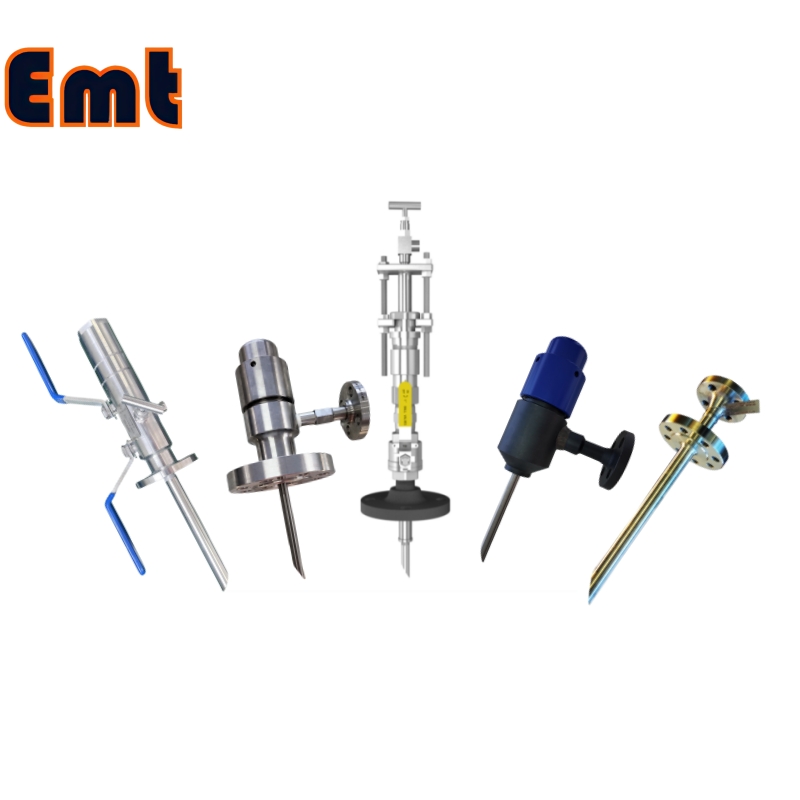
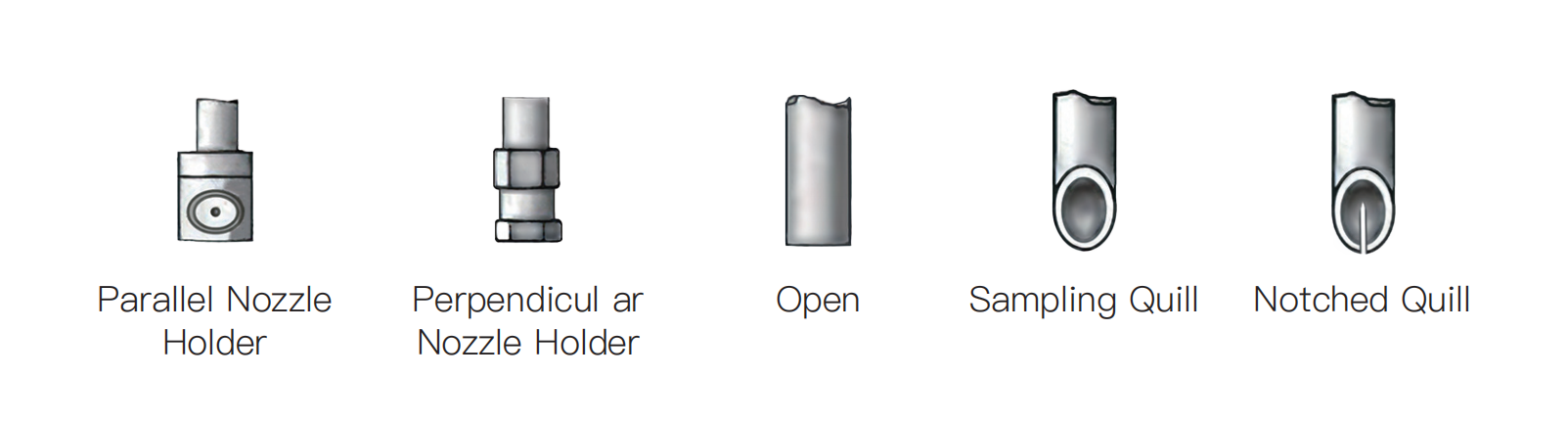
Injection Quill Types
Injection quills are devices used to safely inject chemicals into a pipeline or process stream. The type of quill used depends on the application, direction of flow, and fluid properties.

1. Parallel Nozzle Quill
Orientation: Nozzle runs parallel to the flow of the pipeline.
Use Case: Used when a smooth injection along the flow is needed.
Advantages:
Minimizes disturbance to flow.
Reduces turbulence and backflow.
Applications: Ideal for continuous dosing in high-velocity pipelines.
2. Sampling Quill
Orientation: Designed for extracting samples from the pipeline.
Use Case: Not for injection, but for monitoring, analysis, or testing.
Advantages:
Ensures representative samples from the center of the flow.
Can be retractable for safety and maintenance.
Applications: Water treatment, chemical processing, oil & gas.
3. Open Quill
Orientation: Typically a simple open-ended tube.
Use Case: Used for basic or low-cost applications where precise mixing is not critical.
Advantages:
Cost-effective.
Simple design.
Disadvantages:
May not ensure proper mixing.
Potential for corrosion or wear at the tip.
Applications: Non-critical chemical injection, low-pressure lines.
4. Perpendicular Quill
Orientation: Nozzle is perpendicular to the flow.
Use Case: Used when direct injection across the pipeline is needed.
Advantages:
Promotes better mixing across the flow cross-section.
Useful in slower flow environments.
Applications: Chemical treatment in water lines, flocculant or disinfectant injection.
Summary Table
| Quill Type | Orientation | Main Use | Mixing Efficiency | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel Nozzle Quill | Parallel to flow | Smooth chemical injection | Moderate to High | Continuous dosing in high-velocity lines |
| Sampling Quill | Central extract | Fluid sampling | N/A | Analysis and monitoring |
| Open Quill | Straight open end | Simple injection | Low | Non-critical or low-pressure injection |
| Perpendicular Quill | Perpendicular | Injection into flow path | High | Slow-flow lines needing better mixing |
Working Principle of the Chemical Injection Quill
The chemical injection quill works on basic fluid dynamics principles. It includes a hollow tube or pipe with multiple injection holes. These holes run along the length of the quill.
Next, you install the quill at a key point in the system. This point can be in a pipeline, tank, or reactor. You choose the spot based on where chemical injection is needed.
During operation, pressurized chemical enters the quill through a connection point. The chemical flows into the hollow tube quickly. Then, it exits through the evenly spaced injection holes.
This design spreads the chemical across the system’s cross-section. It ensures complete and even chemical distribution.
Now, velocity and pressure become important. High fluid velocity creates strong, fast-moving jets. These jets generate turbulence inside the process fluid.
As a result, the turbulence mixes the chemical thoroughly. This improves how well the chemical works in the system.
In short, the quill ensures efficient chemical delivery and mixing. It enhances performance and optimizes the overall process.









