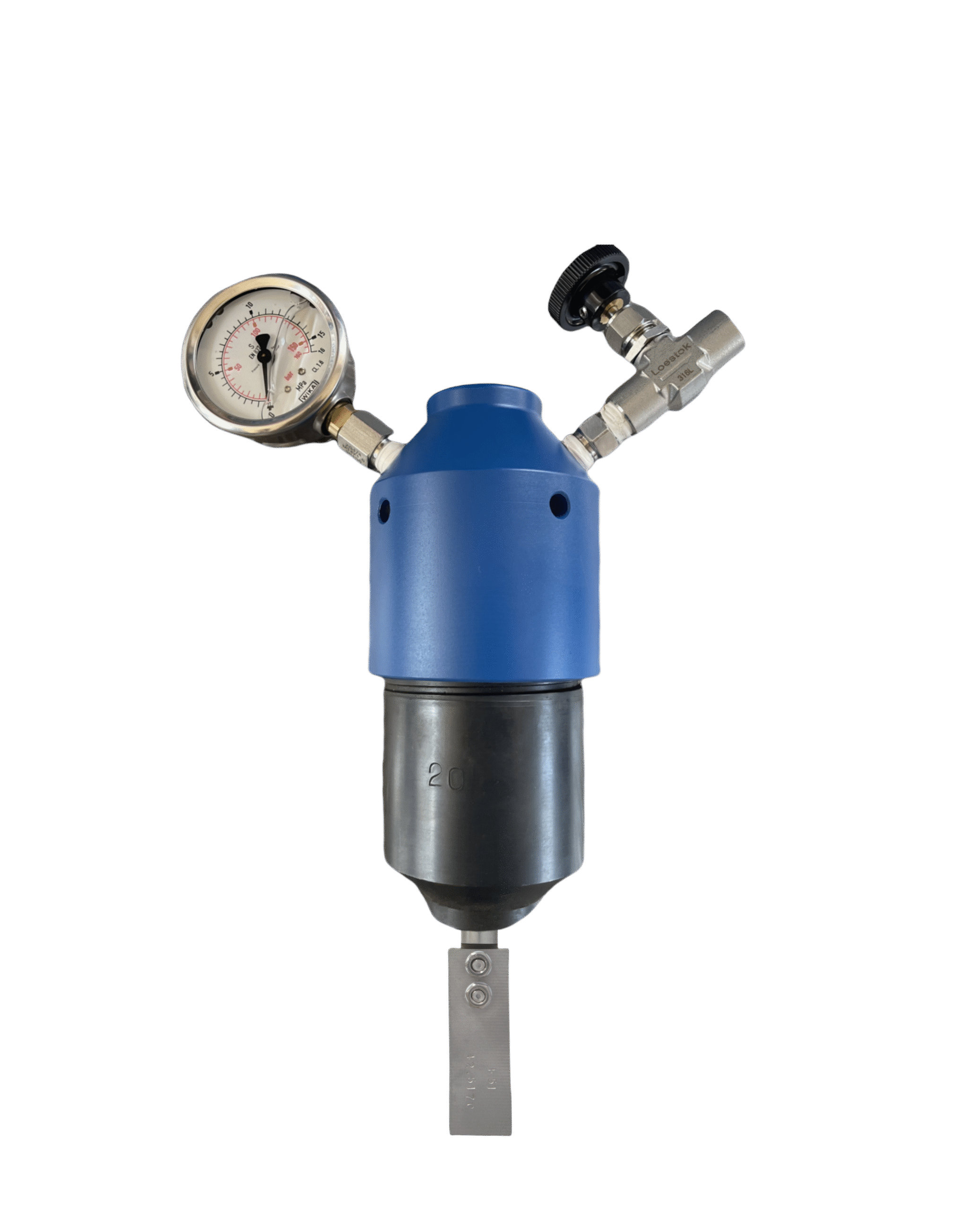
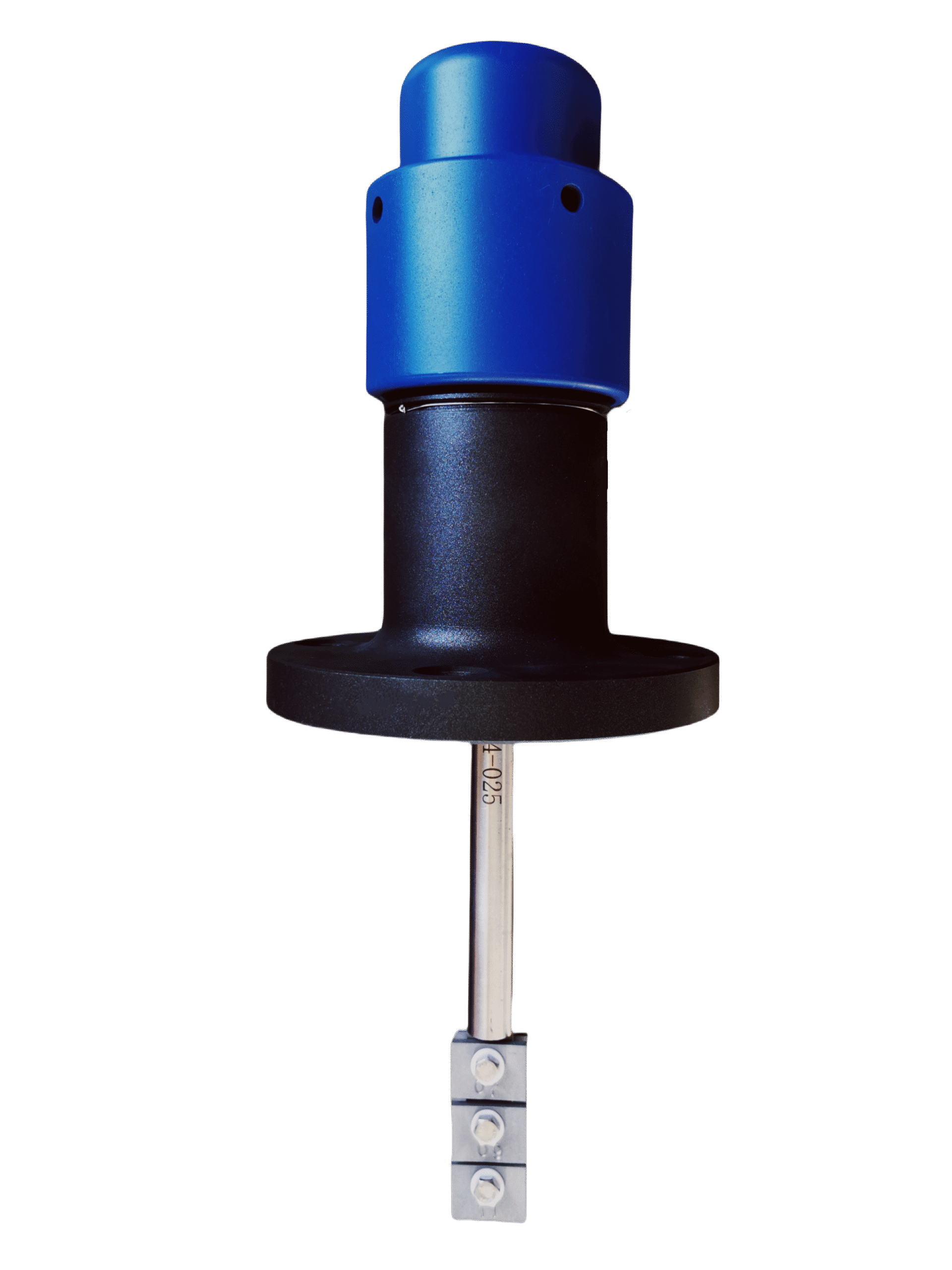
Description
Introduction
Corrosion coupons are straightforward yet effective tools used widely in the industrial sector for monitoring corrosion rates under various conditions. These small, standardized pieces of metal mirror the materials of the system they monitor and experience the same environmental conditions. Periodic checks and measurements of the coupon’s weight help determine the material degradation over time, offering crucial insights into the level of corrosive activity within the system.
In practice, corrosion coupons are small, standardized pieces of metal inserted into pipeline systems to track and quantify corrosion rates across different industries. They endure the same operational conditions for a predetermined duration before being analyzed. Observations of weight loss and physical alterations on the coupons yield data about the environment’s corrosiveness. This data is essential for making informed decisions regarding pipeline maintenance, implementing corrosion prevention strategies, and maintaining system integrity, ultimately helping to reduce costs and enhance operational safety.
Importance of Monitoring Corrosion on Pipelines
Corrosion in pipelines is a major issue that can significantly impact operational efficiency, escalate costs, and create safety hazards. It can cause the deterioration of pipelines, leading to leaks, ruptures, or even complete failures. Such incidents not only disrupt normal operations but also lead to expensive repair or replacement tasks.
Beyond these direct costs, corrosion-induced failures can incur significant indirect expenses, including operational downtime, environmental remediation, potential legal issues, and fines from regulatory bodies. The risks are even greater when pipelines transport hazardous materials, as leaks could result in environmental damage, fires, explosions, or other serious accidents. Therefore, consistent monitoring and management of corrosion are essential to ensure the safety and efficiency of pipeline operations.
Parameters
| Material | Stainless Steel 304、Stainless Steel 316、DSS F51、Carbon Steel A105N、Inconel 625 |
| Operating Temperature | -20±120 |
| Feature | Firstly, Easy to Operating |
| Secondly, High Accuracy Long Life | |
| At last, High Efficiency, Low cost | |
| Payment | TT/LC |
| Advantage | Firstly, they are lightweight and flexible. |
| Secondly, Nice Injection efficiency. | |
| At last, Accurate location tracking. |
How Corrosion Coupons Work on Pipelines
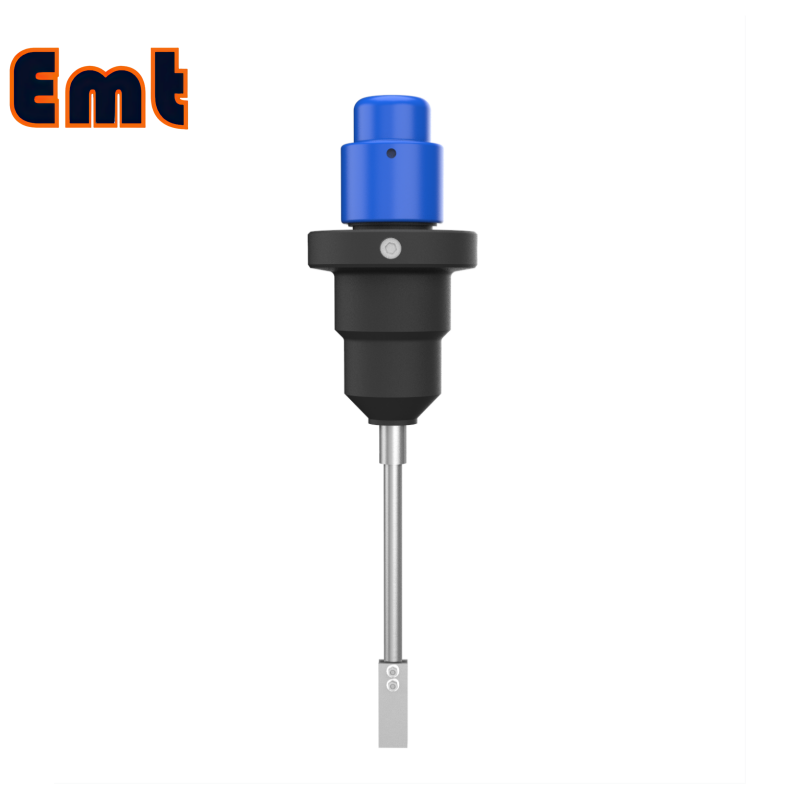
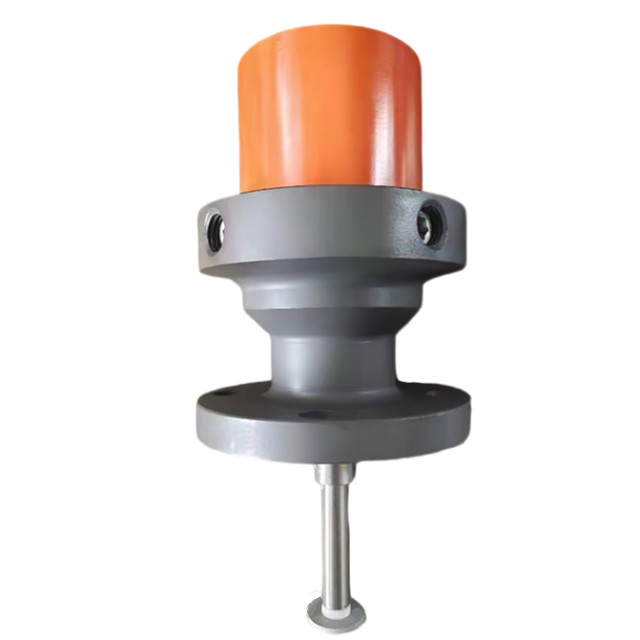
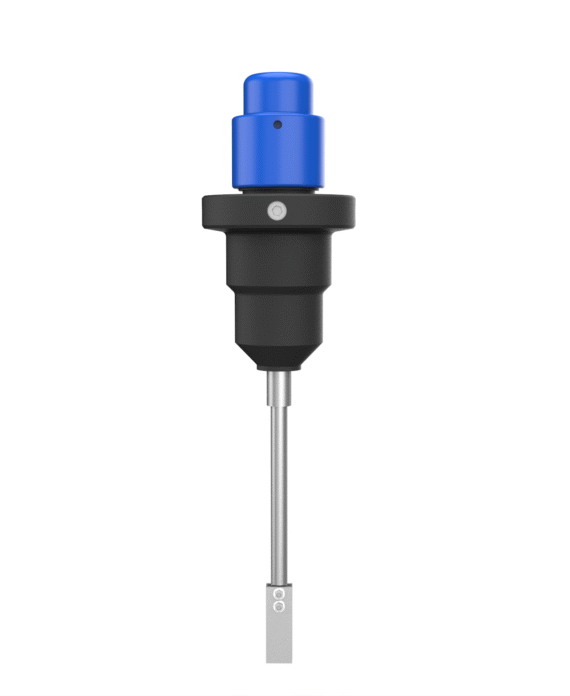
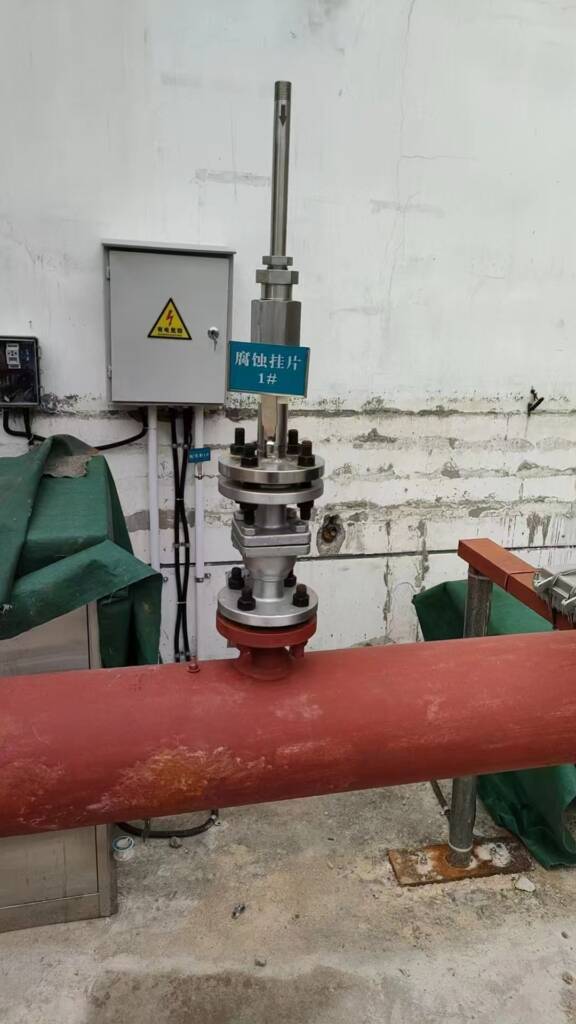
Corrosion Coupons, precisely designed tools, primarily measure the rate of metal deterioration within pipelines in the oil, gas, and water sectors, a process known as corrosion. Manufacturers generally craft these devices as standardized strips, discs, or rods from the same materials as the pipeline itself. The use of Corrosion Coupons involves securing them directly onto the pipeline system, subjecting them to the same environmental conditions as the pipeline. This includes exposure to the same fluids, temperatures, pressures, and flow rates, ensuring that the corrosion they undergo mirrors the actual corrosive conditions within the pipeline.
After being exposed for a set duration, the coupons are removed from the pipeline for detailed evaluation. This evaluation process involves precisely weighing the coupons before and after exposure. This is to calculate the weight loss, a critical measure of corroded metal. In addition to weight loss, the coupons are inspected for physical changes. One such change is pitting—a severe localized corrosion causing tiny holes or cavities. General wear is also examined. Each type of physical change offers specific insights into the corrosion’s nature. This information is valuable for understanding the corrosive environment inside the pipeline.
By analyzing weight loss and physical alterations on the Corrosion Coupons, professionals can assess corrosion rate and type. This information is crucial for developing effective corrosion monitoring and control strategies. These strategies ensure the long-term viability and safety of pipeline operations.
Types of Corrosion Coupons on Pipeline
| Name | Strip Coupon | Multihole Strip Coupon | Disc Coupon |
| Applications | Commonly used for most evaluations. | Use with low-pressure access equipment or through narrow ports that a standard 3/4 inch wide coupon cannot pass. | These circular coupons work in multiple disc monitoring applications. |
| Size | 3”*3/4”*1/16” (76.2mm*19.0mm*3.2mm) |
3”*1/2”*1/16” (76.2mm*12.7mm*3.2) With mounting holes |
Φ1.25”(31.8mm)Thickness 1/16”(3.2mm) |
Strip Coupons on Pipeline
Strip coupons, favored for their high surface area-to-volume ratio, are the most frequently used type of corrosion coupon. This attribute is particularly advantageous for monitoring and assessing the overall corrosion rate. Typically rectangular, these coupons offer a wide and consistent surface for corrosion, allowing for an averaged rate that reflects the general corrosion occurring within the pipeline. Their straightforward design also simplifies installation and removal, making strip coupons a preferred choice in corrosion monitoring.
Cylindrical or Rod Coupons on Pipeline
Cylindrical or rod coupons are tailored for specific uses in corrosion monitoring, especially in systems with active flow conditions. Their shape closely resembles the interior surface of a pipeline, thereby providing an accurate representation of corrosion under actual pipeline conditions. This design is especially useful for examining how fluid velocity and turbulence affect corrosion rates. By replicating the internal conditions of the pipeline, rod coupons offer crucial insights into how flow dynamics influence corrosion, aiding in effective corrosion management.
Disk or Flat Coupons on Pipeline
Disk or flat coupons are typically used for evaluating materials or coatings. These coupons are flat and round, offering a compact corrosion area. They are ideal for testing new materials or protective coatings on pipelines. Using disk coupons enables controlled comparisons of corrosion rates. This provides essential data on performance and suitability for specific pipeline environments.